SO 151
Bremmer
March 28, 1997
First Exam
Part A. Multiple Choice (3 points each). Indicate the best answer in the space provided.
- 1. Which of the following would shift the production possibilities curve inward?
- A. Inefficient use of resources.
B. A reduction in the size of the labor force.
C. An improvement in technology.
D. A change in the combination of goods produced.
E. Both A and B.
- 2. If the production possibilities curve is a straight line:
- A. its slope will always equal -1.
B. it exhibits the law of increasing costs.
C. resources must be equally adaptable at producing either good.
D. resources must be highly specialized.
E. Both B and D.
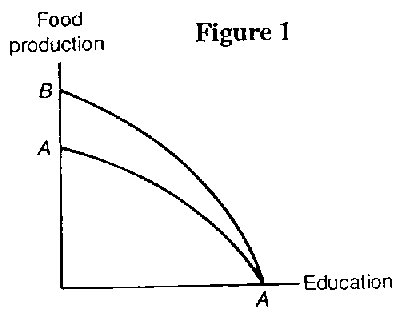
- 3. Which of the following would cause the production possibilities curve in Figure 1 to shift
from AA to BA?
- A. An increase in the size of labor force that affected both food production and education.
B. A disease that affected students' ability to learn (and therefore) education but not food
production.
C. A technological improvement in food production that had no effect on education.
D. A technological improvement in education that had no effect on food production.
E. A drought that affected food production, but had no effect on education.
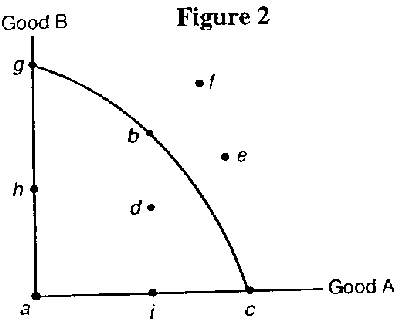
- 4. Which of the following statements about the production possibilities curve in Figure 2 is
false?
- A. If all the economy's resources are used efficiently to produce good A, then the economy is at
point c.
B. Point d represents an inefficient use of resources.
C. Point f is currently unobtainable given the current quantity of resources and level of
technology.
D. If the economy is using its resources fully and efficiently, and it produces more and more of
good B, smaller and smaller amounts of good A must be sacrificed.
E. If the economy is using its resources fully and efficiently, increased production of good A
implies less of good B is being produced.
- 5. For each watch Norway produces, it gives up the opportunity to make 100 pounds of
cheese. Switzerland can produce one watch for every 200 pounds of cheese it produces.
Which of the following is true concerning the comparative advantage between the two
countries?
- A. Norway has a comparative advantage in watches and cheese.
B. Switzerland has the comparative advantage in watches and cheese.
C. Switzerland has the comparative advantage in watches.
D. Norway has the comparative advantage in watches.
E. Norway has the comparative advantage in cheese.
- 6. Suppose a market is in equilibrium and then a price ceiling is established above the
equilibrium price. Which of the following will happen?
- A. Quantity demanded will increase.
B. A surplus will develop.
C. A shortage will develop.
D. The quantity sold will rise.
E. The market will remain at the initial equilibrium.
- 7. Which of the following will cause the demand curve for good X to shift to the right?
- A. A decrease in the price of Y, a substitute for X.
B. A decrease in income, assuming X is a normal good.
C. A decrease in income, assuming X is an inferior good.
D. An increase in the price of Z, a complement good.
E. A decrease in population.
- 8. Which of the following will cause the supply curve for X to shift to the left?
- A. A decrease in the price of inputs.
B. An increase in the number of firms.
C. An improvement in the technology used to produce X.
D. A decrease in the price of X.
E. None of the above.
- 9. If there is an increase in the quantity of roses sold there will have been:
- A. a decrease in demand with no change in supply.
B. a decrease in supply with no change in demand.
C. an increase in demand accompanied by a larger decrease in supply.
D. an increase in supply accompanied by a smaller decrease in demand.
E. None of the above.
- 10. Which one of the following statements best illustrates the concept of diminishing
marginal utility?
- A. A decrease in the price of hamburger will cause consumers to buy more hamburger because
they have, in effect, received an increase in income.
B. If the price of hamburger declines, there will a change in consumer tastes in favor of
hamburger.
C. A typical consumer will receive less satisfaction from consuming hamburgers than from
consuming pork.
D. A typical consumer will receive less additional satisfaction from consuming the fourth
hamburger per week than the third hamburger per week.
E. As the price of hamburger declines, people will substitute away from pork and into hamburger
as pork is now relatively more expensive.
- 11. An increase in supply caused no change in the equilibrium quantity bought and sold.
You correctly deduce that the demand for this product is:
- A. inelastic.
B. perfectly inelastic.
C. perfectly elastic.
D. unitary elastic.
E. elastic.
- 12. If the cross-price elasticity of demand between two goods is positive, we can deduce that
the two goods are:
- A. substitutes.
B. complements.
C. both inferior goods.
D. both luxury goods.
E. both normal goods.
- 13. Along two positively sloped supply curves that are straight lines from the origin:
- A. the price elasticity of supply is the same along both curves.
B. supply is inelastic for all finite prices and quantities on both.
C. supply is less elastic on the steeper curve.
D. the price elasticity of supply is different at different prices and quantities on both lines.
E. supply is more elastic on the steeper curve.
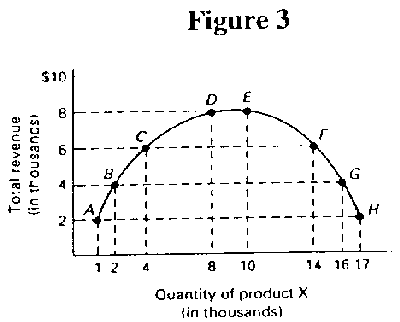
- 14. Referring to Figure 3, when the quantity demanded of X increases from 14,000 to
16,000, the price elasticity of demand for product X is:
- A. elastic.
B. inelastic.
C. perfectly inelastic.
D. unitary elastic.
E. perfectly elastic.
- 15. In Figure 3, at total revenue of $8,000, the price elasticity of demand is:
- A. elastic.
B. inelastic.
C. perfectly inelastic.
D. unitary elastic.
E. perfectly elastic.
Part II. Short Answer (55 points). Give a concise, but complete answer. Use math, graphs,
or equations to help explain your answers. Label all curves and axes. Show your work for
partial credit.
- Describe and illustrate graphically an effective price floor. What are the
consequences of an effective price floor? (10 points)
- A recent breakthrough in the production of laser disk technology has decreased the
cost of laser disks. These disks supposedly will increase the quality of music
recordings tenfold over that available from CDs. Using a demand and supply curve,
what will happen to the price and quantity of laser disks sold? Of CDs sold? (10
points)
- Using a production possibilities curve, discuss the trade off between current
consumption of consumer goods or capital goods, and the implications for economic
growth. (10 points)
- Given the data in the graph below, which nation should specialize in steel
production and which nation in wheat production? Why? What are the limits of
the terms of trade? (10 points)
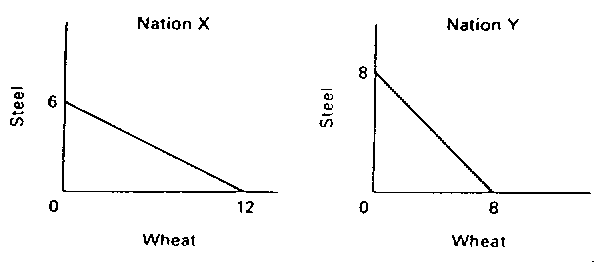
- Assuming no government intervention, describe the market behavior that should
result if the price of a product is below its equilibrium price. (5 points)
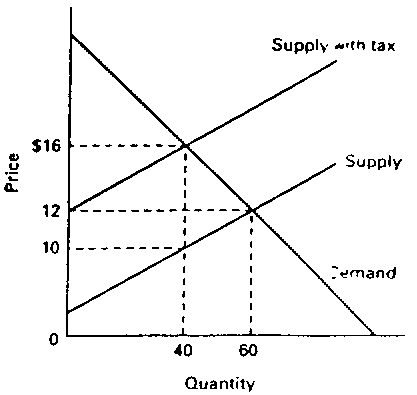
- Use the graph below to answer the following questions. (10 points)
- In the graph below, if the government imposes an excise tax as shown, what
is the tax burden on the sellers? on the buyers? Explain.
- Using the initial and final equilibrium prices on the graph, calculate the price
elasticity of demand using the arc formula. Is demand elastic, inelastic, or
unitary elastic?