SL 151
Bremmer II
April 21, 2000
2nd In-Class Exam - - Chapters 7-9, 13-14
Part I: Multiple Choice (3 points each). For each of the following
questions, indicate the best answer.
Questions 1 - 3 refer to Figure 1 which represents a constant-cost,
perfectly competitive industry and a firm in the industry.
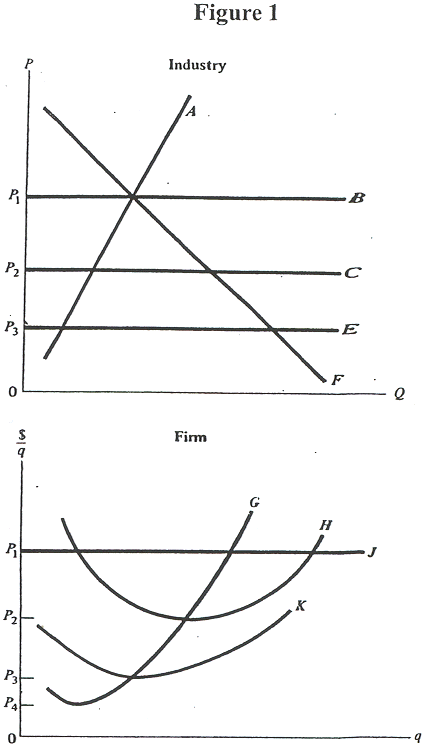
- According to Figure 1, in the long run:
- there will be no entry or exit of firms in this industry.
- firms will enter and curve F shifts to the right.
- firms will exit and curve F shifts to the left.
- firms will exit and curve A shifts to the left.
- firms will enter and curve A shifts to the right.
- In Figure 1, long-run equilibrium in the industry will be reached
at a price of:
- P1
- P2.
- P3.
- P4.
- Referring to Figure 1, the industry's long-run supply curve is:
- curve A.
- curve F.
- curve B.
- curve C.
- curve E.
- If the government impose a $100 lump-sum tax on a firm:
- its ATC, AFC, and MC curves shift upwards, but its AVC curve
is unaffected.
- its ATC, AVC, and MC curves shift upwards, but its AFC curve
is unaffected.
- its ATC and AFC curves shift upwards, but its MC and AVC
curves are unaffected.
- its ATC and AFC curves shifts downwards, but its MC and AVC
curves are unaffected.
- its ATC, AVC, and MC curves shifts downwards, but its AFC
curve is unaffected.
- Assume a firm's labor union agrees to a wage cut. Then the
firm's:
- ATC, AFC, and MC curves will shift downwards, but its AVC
curve is unaffected.
- ATC and AVC curves will shift downwards, but its AFC and
MC curves are unaffected.
- ATC and MC curves will shift downwards, but its AFC and AVC
curves are unaffected.
- ATC and AFC curves shifts downwards, but its MC and AVC curves
are unaffected.
- ATC, AVC, and MC curves shifts downwards, but its AFC curve
is unaffected.
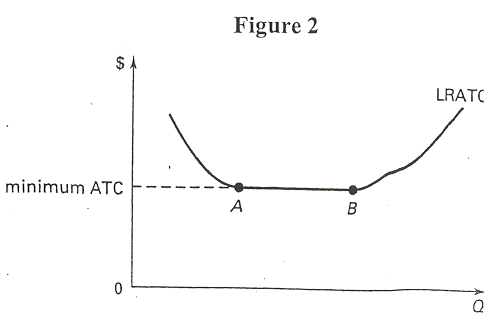
- In Figure 2, the long-run average total cost curve (LRATC) indicates
that there are diseconomies of scale:
- between points A and B.
- at points A and B.
- to the left of point B.
- to the right of point B.
- to the left of point A.
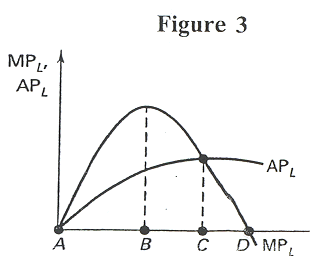
- In Figure 3, what level of labor usage maximizes output?
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- Can't tell with the information given.
- In Figure 3, at what level of labor does diminishing returns sets
in?
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- Can't tell with the information given.
- In Figure 3, when is AVC rising?
- Only between A and B.
- Only between A and C.
- To the right of point C.
- Only between B and D.
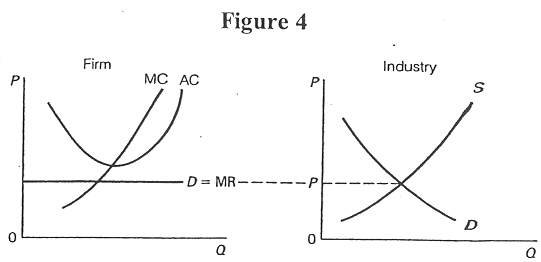
- Assume Figure 4 shows a perfectly competitive, increasing-cost
industry in short run equilibrium (Note: AC = ATC). What will happen
in this industry in the long-run?
- Firms will enter and S will shift to the right.
- Firms will exit and S will shift to the left.
- The MC and the ATC curves will shift down.
- A and C.
- B and C.
- When marginal cost is increasing:
- average variable cost must be increasing.
- average total cost must be increasing.
- total cost is increasing.
- average fixed cost is increasing.
- marginal product is increasing.
- Given a normal, upward-sloping supply curve, suppose that the
demand for French bread decreases. What will happen to producer surplus
in the market for French bread?
- It increases.
- It decreases.
- It is unaffected by this change in demand.
- It decreases briefly, then increases.
Figure 5 shows the before-trade and after-trade position of Spain
in the oil market.
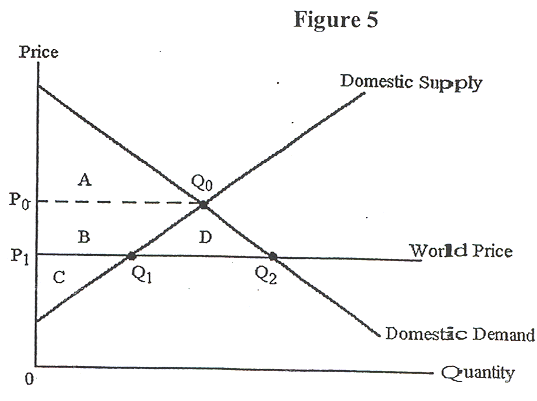
- According to Figure 5, before trade, consumer surplus in Spain
was:
- C.
- C + B.
- A + B.
- A + B + C.
- A.
- In Figure 5, after trade, producer surplus falls from ____ to
____ .
- A + B + C; C
- A + B + C; B + C
- C + B + D; C + B
- C + B; C
- C + B + D; C
- Given the information in Figure 5, after trade, society welfare
___ by ___ .
- increases; B + D
- increases; D
- decreases; B
- increases; A + B + D + C
- decreases; C
Part II. Short-Answer Questions (55 points). Give a concise,
but complete answer for each of the following questions. When appropriate,
use math, graphs, or equations to help explain your answers.
- Suppose a firm has the short-run production function listed below.
Calculate the average product and the marginal product for this production
data. Do you feel such a short-run production is plausible? Why or why
not? (10 points)
| Q |
0 |
30 |
60 |
90 |
120 |
150 |
180 |
210 |
240 |
270 |
| L |
0 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
50 |
60 |
70 |
80 |
90 |
| AP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| MP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- "A perfectly competitive firm will never operate in the short-run
at an output where its average total cost curve is downward sloping." True
or false? Explain. (10 points)
- Describe how the long-run average cost curve is derived. Why does
a firm need to know its long-run average cost curve? Explain which plants
would be used over- and under- capacity. Identify the optimal sized plant
and tell why its optimal. (15 points)
- Starting from long-run equilibrium, trace the short-run and long-run
effects of a decrease in demand for a perfectly competitive, constant-cost
industry. (10 points)
- Assume a market has a downward-sloping demand curve and an upward-sloping
supply curve. Using a demand and supply diagram, illustrate and explain
what happens to consumer surplus, producer surplus, and society welfare
after the imposition of a $1 excise tax on producers. (10 points)




