SL 151 Name
_________________________________________ CM ______
Bremmer I
1st
In-Class Exam - - Chapters 1-3, 18
Part I. Multiple Choice (3 points). For each
question, indicate the best answer in the space provided.
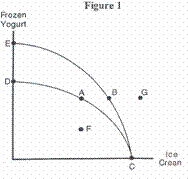
___ 1. Given
production possibilities curve DC in Figure 1, point B indicates a bundle of
goods:
A. where the
economy is at full production and full employment.
B. that involves
inefficient production and excessive unemployment.
C. that is
beyond society’s current productive capabilities.
D. that society
may be able to consume given free trade with another country.
E. Both C and
D.
___ 2. Referring
to Figure 1, a shift in the production possibilities curve from DC to EC could
be due to a:
A. technological
improvement in the production of ice cream.
B. technological
improvement in the production of both goods.
C. reduction in
the rate of unemployment towards full employment.
D. technological
improvement in the production of frozen yogurt.
E. fall in the
demand for frozen yogurt.
___3. The production possibilities curves in
Figure 1 imply that:
A. resources in
the economy are not specialized and they can be freely moved between the
production of ice cream and frozen yogurt.
B. as the
production of frozen yogurt increases along a given PPC, its opportunity cost
is constant.
C. as the
production of increase cream increases along a given PPC, increasing amounts of
frozen yogurt must be given up.
D. production of
point F is impossible given current technology and resources.
E. Both A and
B.
Figure 2
shows the production possibilities curves for two countries - - Nation X and
Nation Y.
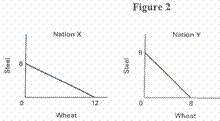 ___ 4. Given
Figure 2, which of the following statements is true?
___ 4. Given
Figure 2, which of the following statements is true?
A. Both Nations
X and Y exhibit the law of increasing cost.
B. The
opportunity cost of producing steel in Nation X is greater than the opportunity
cost of producing steel in Nation Y.
C. In Nation Y,
the opportunity cost of one more unit of wheat is ˝ unit of steel.
D. Neither
country would gain from international trade.
E. Nation Y has
a comparative advantage in steel production.
___ 5. Which
of the following would cause an outward shift in a production possibilities
curve?
A. A decrease in
the size of the labor force.
B. A fall in the
unemployment rate towards the full employment level.
C. The
destruction of capital.
D. An increase
in education and job training.
E. Society
decides to produce more of one good and less of the other.
___ 6. If
the government sets a price floor below the equilibrium price, then:
A. firms’
revenues will fall. D. neither
a shortage nor a surplus occurs.
B. a shortage
results. E. Both
A and B.
C. a surplus
occurs.
In Figure 3,
the initial demand and supply curves of ground beef were D and S, respectively. Assume the demand and supply curves
simultaneously shift to D' and S', respectively.
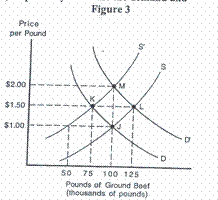
___ 7. Regarding
Figure 3, which of the following would cause the demand curve to shift from D
to D'?
A. A decrease in
the price of beef.
B. A decrease in
the price of chicken, a substitute for beef.
C. An increase
in the price of wine, a complement for beef.
D. A decrease in
consumer income, assuming beef is a normal good.
E. None of the
above.
___ 8. Regarding
Figure 3, which of the following would cause the supply curve to shift from S
to S'?
A. A decrease in
the price of beef.
B. A decrease in
the price of cattle feed, an input for beef.
C. Ranchers
expect the future price of beef to fall.
D. A decrease in
the number of firms producing beef.
E. An increase
in the per pound subsidy that ranchers received from the government.
___ 9. A
decrease in both the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity could be
caused by a(n):
A. decrease in
supply.
B. simultaneous
decrease in supply and increase in demand.
C. simultaneous
increase in both demand and supply.
D. increase in
demand.
E. a
simultaneous increase in demand and decrease in supply.
___ 10. Given
a perfectly inelastic demand curve, a government subsidy of $2 per unit causes
the equilibrium price:
A. to fall by
less than $2 per unit. D. to
increase by more than $2 per unit.
B. to fall by
more than $2 per unit. E. to
increase by exactly $2 per unit.
C. to fall by
exactly $2 per unit.
___ 11. Given
a negatively sloped, linear demand curve, as price increases:
A. revenue
always increases. D. the
price elasticity of demand increases.
B. the price
elasticity of demand remains constant. E. revenue
always decreases.
C. the price
elasticity of demand decreases.
___ 12. Which
of the following is characteristic of an elastic demand curve?
A. The product has
a small number of viable substitutes.
B. Consumers
have a longer time period to adjust to a price change
C. Only a small
percentage of the consumers’ budget is spent on the good.
D. Consumers view
the product as a luxury good.
E. None of the
above characteristics are consistent with a good having elastic demand.
___ 13. Assume
good Y has a negative income elasticity of demand and a perfectly elastic
supply. Holding everything else
constant, how will an increase in consumers’ incomes affect the market for Y?
A. The
equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity of Y both increase.
B. The
equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity of Y both decrease.
C. The
equilibrium quantity of Y remains constant, but the equilibrium price of Y
falls.
D. The
equilibrium price of Y remains constant, but the equilibrium quantity of Y
falls.
E. The
equilibrium price of Y increases, while the equilibrium quantity of Y falls.
___ 14. Given
a linear demand curve, could an increase in supply ever cause no change in
total revenue?
A. Yes, if the
arc formula shows the price elasticity of demand between the two prices is
elastic.
B. Yes, if the
arc formula shows the price elasticity of demand between the two prices is
inelastic.
C. Yes, if the
arc formula shows the price elasticity of demand between the two prices is unitary
elastic.
D. Only if the
demand was perfectly inelastic.
E. Only if the
demand was perfectly elastic.
___ 15. If an
increase in the price of Y causes the demand for X to shift to the right, then:
A. X and Y are
complements, and the cross-price elasticity of the demand for X with respect to
the price of Y is positive.
B. X and Y are
complements, and the cross-price elasticity of the demand for X with respect to
the price of Y is negative.
C. X and Y are
substitutes, and the cross-price elasticity of the demand for X with respect to
the price of Y is positive.
D. X and Y are substitutes,
and the cross-price elasticity of the demand for X with respect to the price of
Y is negative.
E. X is a
normal good and the income elasticity of demand for X is positive.
Part
II. Multiple Choice (55 points). Give a concise,
but complete answer for the following questions. When appropriate, use math, graphs, and
equations to help explain your answers.
Label your graphs.
1. Assume an economy with specialized
resources produces tanks and cars. Holding everything else constant, what
happens to the production possibilities curves as natural resources are depleted? Is society better or worse off? Given the continued depletion of natural
resources, why is sustained technological improvement important to society
welfare? (15 points)
 2. What happens to the current market price
and the current market quantity of a company’s stock if current owners and
potential investors expect the price of the stock to fall in the future? Explain your answer using a demand and supply
diagram. (10 points)
2. What happens to the current market price
and the current market quantity of a company’s stock if current owners and
potential investors expect the price of the stock to fall in the future? Explain your answer using a demand and supply
diagram. (10 points)
3. Answer the following questions using Figure
4. (15
points)
A. Using the demand curve shown in Figure 4,
compare the price elasticity of demand between 14 and $12 and between $6 and
$4. Use the arc or midpoint formula in
your calculations. In each price range
is demand elastic, inelastic, or unitary elastic? (10
points)
B. Referring to Figure 4, is demand elastic,
inelastic, or unitary elastic between points U and V? Why? (5 points)
4. Answer the following questions referring to
the following production possibilities curves for Nation A and
Nation B. Show your work for partial credit. (15
points)
|
Nation A’s
Production Possibilities |
|
Nation B’s
Production Possibilities |
||||||||||
|
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
|
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
|
Good X |
60 |
45 |
30 |
15 |
0 |
|
Good X |
20 |
15 |
10 |
5 |
0 |
|
Good Y |
0 |
15 |
30 |
45 |
60 |
|
Good Y |
0 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
A. What is the opportunity cost of Nation A
producing one more unit of Good X? (3 points)
B. What is the opportunity cost of Nation B
producing one more unit of Good Y? (3 points)
C. Nation A has a comparative advantage in
which product? (2 points)
D. Nation B has a comparative advantage in
which product? (2 points)
E. What is a feasible terms of trade at which
foreign trade is mutually beneficial? (3 points)
F. How much of Good X and Good Y is produced
after trade? (2 points)