Quiz
Your daily quiz needs taken care of in one convenient location!
Previous quizzes appear here in reverse chronological order.
Lesson 36
Consider the triangular plate shown below. Each square on the grid is 1 cm×cm.
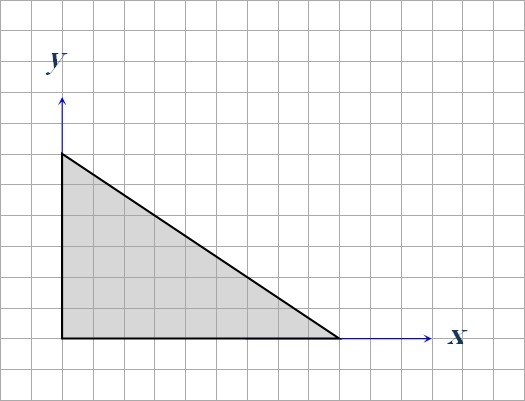
- The x coordinate of the x-centroid is closest to
- The shaded area to the left of the x-centroid is the same as the shaded area to the right.
Lesson 33
The surface between the block and the inclined plane is rough. (I.e., it is subject to friction.) The block is in static equilibrium.
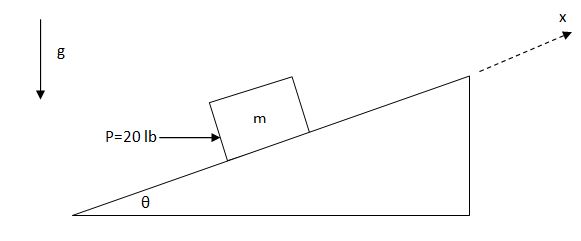
- The magnitude of the normal force between the block and the inclined plane is
- Since the block is in static equilibrium, the friction force between the block and the surface is f = μsN
- In this problem the friction force will act
Lesson 32
A pulley with a crank is shown in the figure below. A student has created a FBD for this system as shown.
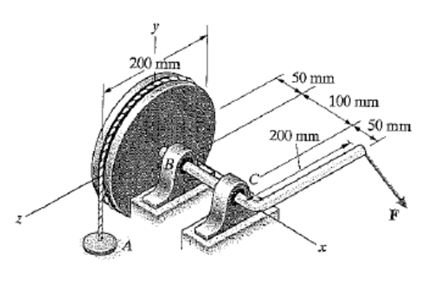
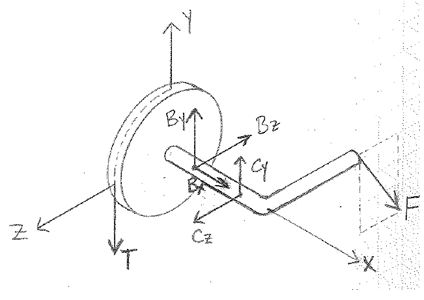
The student has also determined that the moments about point C due to the force and the reaction at B are, respectively,
and
r × B = -100Bz j - 100By k [N-mm].
- Given that the tension force T is vertical, what is the correct expression for the moment arm (i.e., r) to find the moment due to T about point C?
- What is the correct expression for the moment due to T about point C?
- What is the magnitude of T?
Lesson 29
Recall the two trusses from our example:
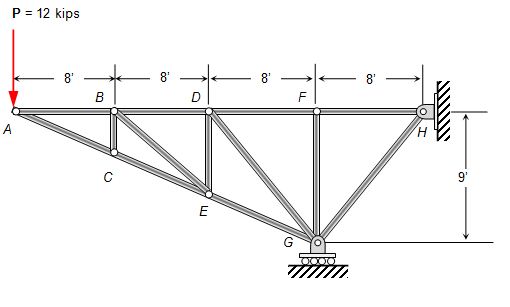
- How does the force in member BC compare for the two loadings?
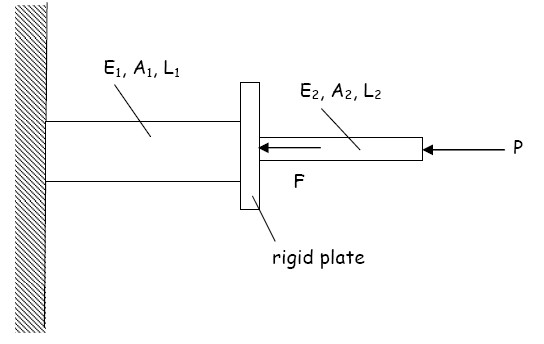
- Is this system statically determinate? All components are weightless and the wall is rigid.
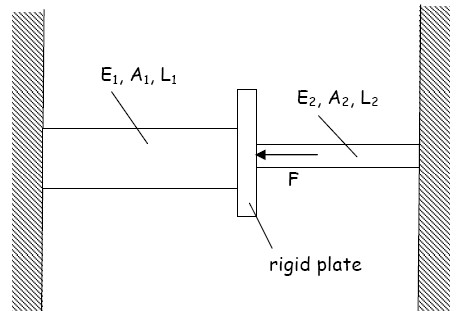
- Is this system statically determinate? All components are weightless and the walls are rigid.
Lesson 27
Lesson 22
A frame is loaded as shown in the figure.
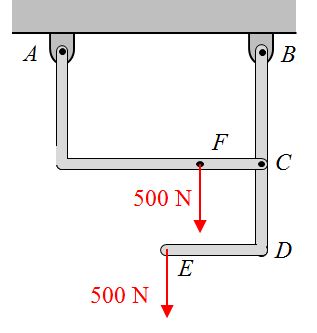
A free body diagram of the frame is given by
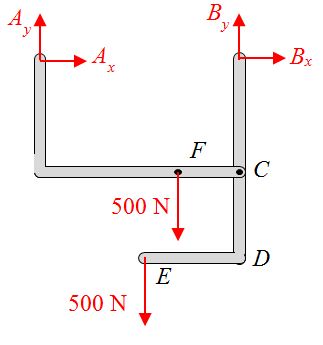
A free body diagram of piece AC is given by
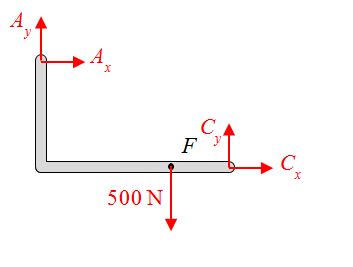
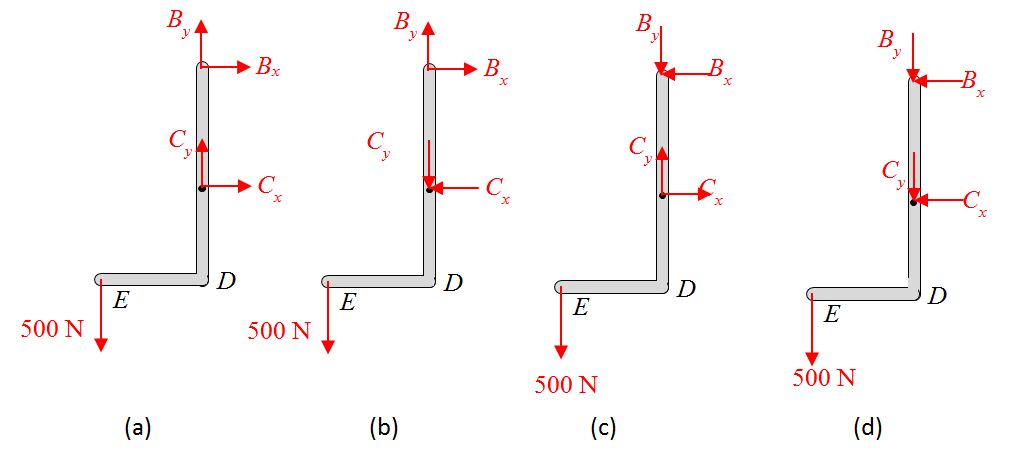
Which of the following free body diagrams is correct for piece BDE?
Lesson 21
Three pipes all of weight W rest in a weightless pipe rack as shown in the figure.
- Which figure gives the correct free body diagram of the pipes and the rack together?
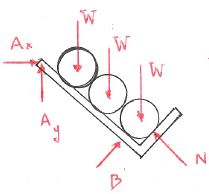
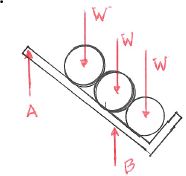
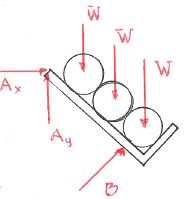
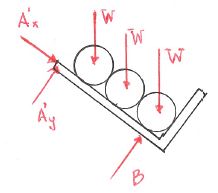
a. b. c. d. - Which figure gives the correct free body diagram of the bottom pipe?
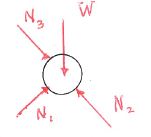
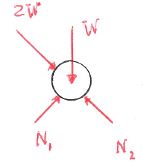
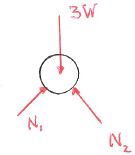
a. b. c.
Lesson 19
Consider the two booms shown in the figure. There are massless and frictionless pulleys at C and D.
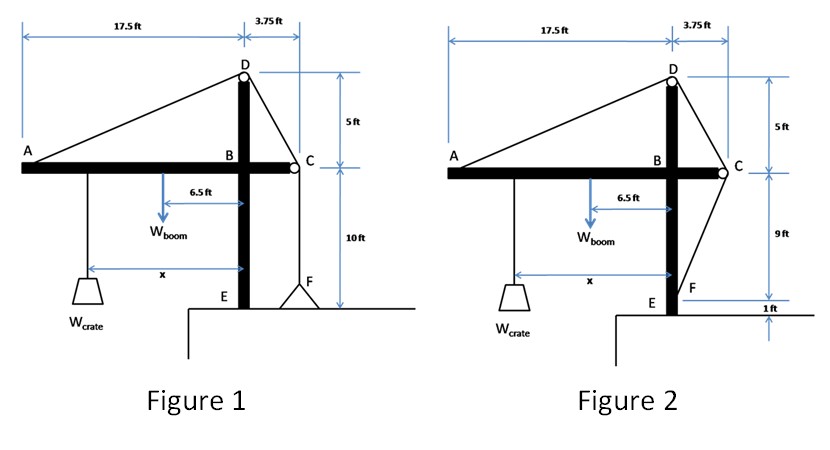
- How does the tension in the cable compare for the two cases?
Lesson 18
- Consider drawing a free body diagram in which you must "cut" a massless cable. How many unknown reactions does cutting the cable introduce?
- Consider drawing a free body diagram in which you must "remove" a 2-D pin connection. How many unknown reactions does this introduce?
- Consider drawing a free body diagram in which you must "remove" a 3-D ball and socket joint (like your shoulder) from a body. How many unknown reactions does this introduce?
- Consider drawing a free body diagram in which you must "cut" through a 3-D cantilever beam where it is attached to a wall. How many unknown reactions does this introduce?
Lesson 15
- For a moment about point P due to a force F, MP = r×F.
- For a moment about point P due to a force F, MP = F×r.
- For a moment about point P due to a force F, MP makes a right angle with r.
- For a moment about point P due to a force F, MP makes a right angle with F.
- A force of 10 N is applied at point B. We wish to maximize the moment about point A due to the force at B. At what angle,θ, shall we place the force at B?
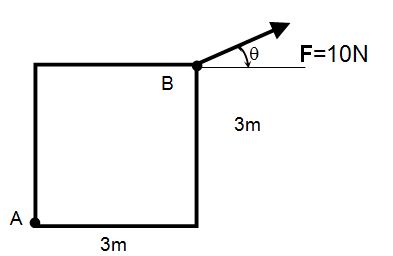
Lesson 14
- For a moment about point P due to a force F, MP = r×F.
- For a moment about point P due to a force F, MP = F×r.
- For a moment about point P due to a force F, MP makes a right angle with r.
- For a moment about point P due to a force F, MP makes a right angle with F.
- A force of 10 N is applied at point B. We wish to maximize the moment about point A due to the force at B. At what angle,θ, shall we place the force at B?

Lesson 14
A compound bar is loaded as shown in the figure.
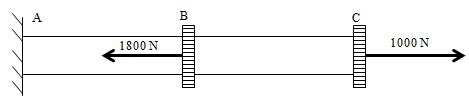
- What is the magnitude of the axial force in Bar AB?
- Bar AB is in...
- Under this loading Bar AB will...
Lesson 11
A massless bar with Young's modulus E, length L and cross sectional area A is welded in place between two rigid plates. A weight W is then hung from a pin on the bar.
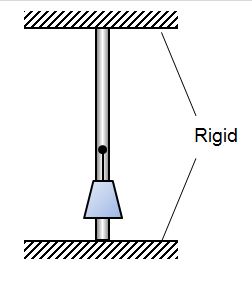
- Which figure gives the correct free body diagram for the bar?
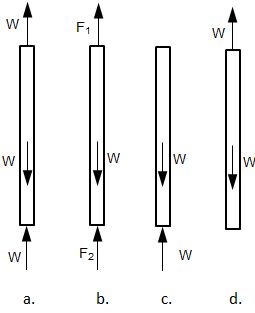
- Which figure gives the correct free body diagram for the section of bar above the pin?
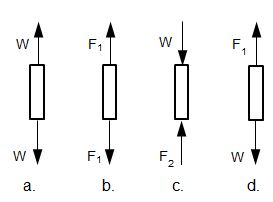
- What is the total deflection for the whole bar?
- The equilbrium equations by themselves are sufficient to solve for all unknown forces.
Lesson 10
Two metal bars are made of different materials but have identical geometry (dimensions) and identical tensile loading.
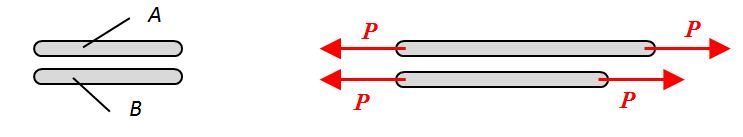
- At the applied load, Bar A deflects more than bar B. When load is removed, both bars return to their original dimensions. Therefore, the metal in bar A is
- In a second test, the bars are identically loaded until one bar fails. The bar that fails first is
- Rubberbands are
Lesson 9
- A pinned link is loaded axially through its pins only.
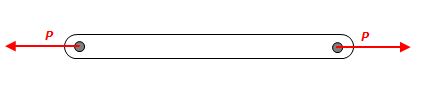
True/False: There is only normal stress (σ) and no shear stress (τ) in the link
- In order to calculate the shear stress in the pin, what area do you use?
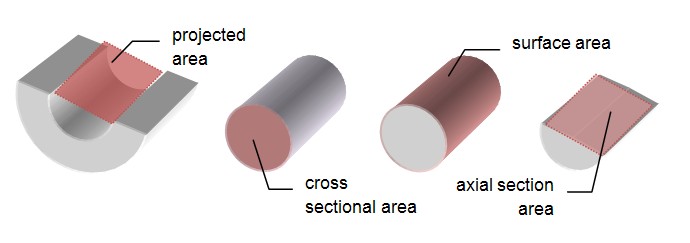
- Stress is a...
Lesson 8
- A four-legged table rests on a floor. The table legs all have circular cross sections with 1-in diameters. With the intent of lessening damage to the floor, 2-in diameter disks are placed under each leg. With the addition of the disks, the contact stress on the floor will...
- Weights in a weight room are stacked on a spindle with a rubber mat as the base. With the intent of lessening damage to the floor, the facility director replaces the mat with a rubber mat twice as thick. For the same weight stack, the contact stress on the floor will...
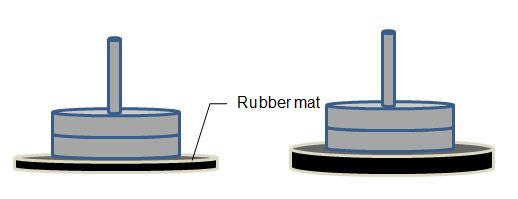
Lesson 7
A hydraulic cylinder slowly pushes the frictionless pulley as shown in the figure.
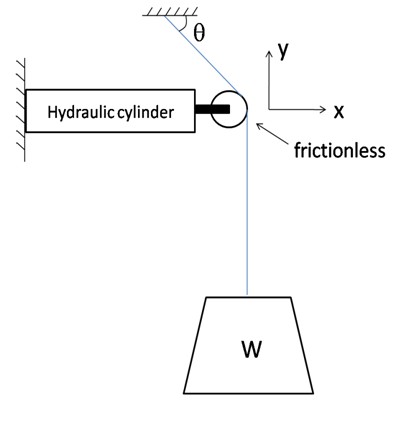
- As θ decreases, what happens to the tension in the cable?
- Did you sketch a free body diagram to help you answer part a?
Lesson 6
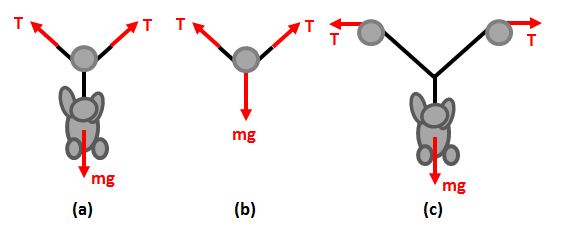
A gorilla is suspended from a cable making use of frictionless pulleys as shown in the figure.
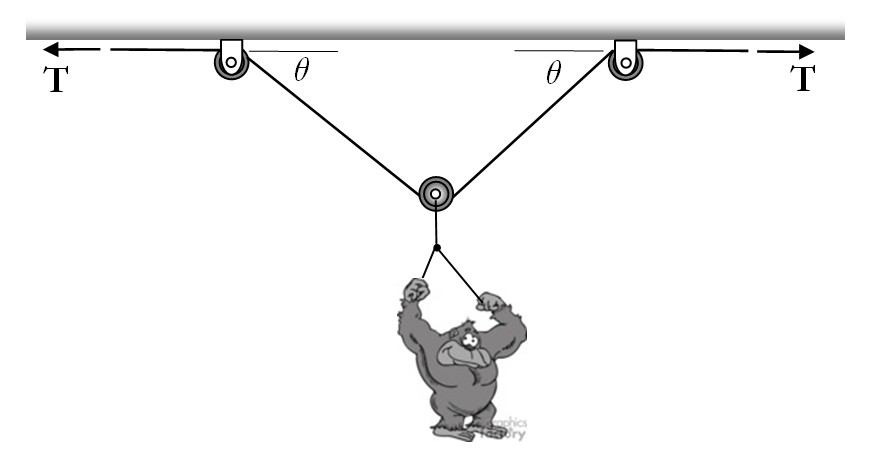
- Which figure gives the best free body diagram for the system?
- As θ decreases, what happens to the tension in the cable?
Lesson 5
A particle is defined as an object with mass but no size. A consequence of something being a particle is that all the forces acting on it pass though a single point.
Can a bowling ball be treated as a particle?
- What is true of a particle in static equilibrium?
- In the first figure a person pulling on the rope results in a tension of 100 lb. With a person exerting a 100 lb force on each end of the rope as shown in the second figure, the tension in the rope will be

Lesson 4
- Consider a unit vector given by e = exi + eyj + ezk. What is the magnitude of (ex2 + ey2 + ez2)½?
- What are the dimensions of e?
- What is the angle e makes with the z-axis?
Lesson 2
Consider the figure below in which the top view of a fence post is shown. Both F1 and F2 have a magnitude of 100 lb.
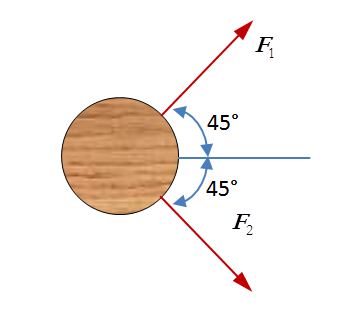
-
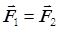
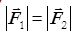
- The magnitude of the resultant of the two forces is closest to