13. Computing the Spectrum
Throughout this text, as we studied sampling, linear filtering, and modulation, we have seen the value of frequency domain analysis. The spectrum concept is fundamental to this way of thinking about signals and systems.The primary goal of this chapter is to show how an FFT-computed spectrum relates to the true spectral content of a signal given by the Fourier transform integral.
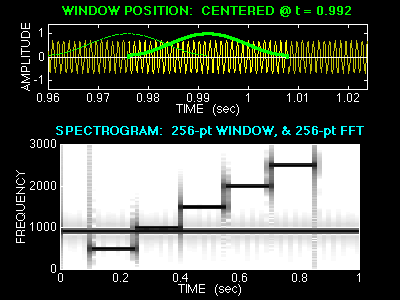
A secondary goal is to introduce the rudimentary ideas of what is commonly called time-frequency analysis. In one type of time-frequency analysis, we analyze a very long signal by doing many short FFTs, which are then assembled into a single gray-scale image, called a spectrogram. The resulting image shows the spectrum analyst how a localized frequency spectrum changes with time.
Homework
Labs - MATLAB
| Lab 17: Digital Communication: FSK Signals (Encoding) |
Perhaps an apt title for this quick introduction to
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Modems would be everything
you wanted to know about FSK Modems but were afraid to ask!
The goal of this lab (and the next one) is to understand a simple modem,
the Frequency Shift Keying
(FSK) Modem, referred to by the International Telecommunications Union
(I.T.U.) as V.21.
This lab presents how to construct the FSK encoder. |
| Lab 18: Digital Communication: FSK Signals (Decoding) |
Perhaps an apt title for this quick introduction to
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Modems would be everything
you wanted to know about FSK Modems but were afraid to ask!
The goal of this lab (and the previous one) is to understand a simple modem,
the Frequency Shift Keying
(FSK) Modem, referred to by the International Telecommunications Union
(I.T.U.) as V.21.
This lab presents how to decode FSK signals. [Files] |
| Lab 19: The Fast Fourier Transform | The goal of this lab is to introduce the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) for efficient computer calculation of the Fourier Transform and then to investigate some of the Fourier Tranform's properties. |
| Lab 20: Extracting Frequencies of Musical Tones |
 This lab is built around a single project that involves the implementation
of a system for automatically writing a musical score by analyzing the
frequency content of a recording (a sampled signal).
A primary component of such a system is the spectrogram which produces a
time-frequency representation of the recorded waveform.
However, to make a working system, several other processing components are
needed after the spectrogram to extract the important information related
to the notes.
The design of these additional blocks will lead naturally to a deeper
understanding of what the spectrogram actually represents.
[Files]
This lab is built around a single project that involves the implementation
of a system for automatically writing a musical score by analyzing the
frequency content of a recording (a sampled signal).
A primary component of such a system is the spectrogram which produces a
time-frequency representation of the recorded waveform.
However, to make a working system, several other processing components are
needed after the spectrogram to extract the important information related
to the notes.
The design of these additional blocks will lead naturally to a deeper
understanding of what the spectrogram actually represents.
[Files]
|